Oral Cancer Treatment
- Home |
- Oral Cancer Treatment
Oral Cancer Treatment
Types
- Precancerous Lesions
- Precancerous Conditions
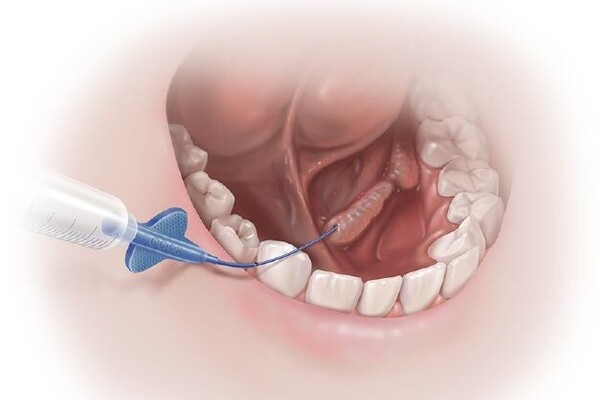
Oral Cancer Treatment
Oral cancer treatment typically involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the stage and location of the cancer. Early-stage cancers may be treated with surgery alone, often using techniques like Mohs surgery to remove cancerous tissue while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible. For more advanced stages, a combination of surgery and radiation therapy is common, and chemotherapy may be added to target cancer cells more effectively. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are newer options that may be considered in certain cases. Regular follow-up care is crucial to monitor for any signs of recurrence and manage side effects of treatment.
Precancerous Lesions
Precancerous lesions are abnormal growths or sores in the oral cavity that have the potential to develop into cancer if left untreated. They are often identified through routine dental examinations and biopsies. Treatment usually involves the removal of these lesions through surgical excision, laser therapy, or cryotherapy to prevent progression to oral cancer, along with regular monitoring for any signs of recurrence.
Precancerous Conditions
Precancerous conditions refer to changes in the tissues of the mouth that increase the risk of developing oral cancer. These conditions can include leukoplakia (white patches), erythroplakia (red patches), and submucous fibrosis, among others. Early detection and management are crucial, and treatments may involve lifestyle changes, medication, or surgical interventions to address the underlying causes and prevent malignant transformation.

20 +
years experience
FAQs
What are basal implants and how do they differ from traditional implants?
Basal implants are a type of dental implant that utilizes the dense cortical bone in the basal region of the jaw for stability. Unlike traditional implants, basal implants are single-piece implants that do not require bone grafts or sinus lifts, making them suitable for patients with insufficient bone volume or density. They also allow for immediate loading, meaning permanent teeth can be fixed in less than a week after the implant surgery.
Are basal implants suitable for everyone?
Basal implants are generally suitable for patients with moderate to severe bone atrophy, including those who are diabetic, hypertensive, or smokers. However, they may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions, such as recent myocardial infarction or stroke, or those taking medications that inhibit blood clotting. It's best to consult with a dental professional to determine if basal implants are the right option for you.
What is maxillofacial surgery and what conditions does it treat?
Maxillofacial surgery is a specialized type of surgery that focuses on the face, jaw, neck, and mouth. It treats a variety of conditions, including jaw pain, limited jaw function, tooth impaction, oral diseases, abnormal bites, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, facial injuries, cleft lips and palates, and tumors or cysts in the head and neck area
What is the recovery process like after maxillofacial surgery?
Recovery after maxillofacial surgery varies depending on the specific procedure. Generally, you may need to follow a liquid or pureed diet for about 4 to 6 weeks, and you might experience some swelling and discomfort. Your surgeon will provide specific post-operative care instructions, and it's important to follow them closely to ensure proper healing
How often should I get a dental checkup?
It's recommended to visit your dentist every six months for a routine checkup and cleaning. However, based on your oral health, your dentist might suggest more frequent visits.
What are the best ways to practice good oral hygiene at home?
Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, use an antiseptic mouthwash, eat a balanced diet, and avoid tobacco.
How can I improve the whiteness of my teeth?
You can improve teeth whiteness by practicing good oral hygiene, avoiding staining foods and beverages, and considering professional whitening treatments or over-the-counter whitening products recommended by your dentist.
Why should I have dental X-rays taken?
Dental X-rays help identify hidden dental issues such as cavities, impacted teeth, bone loss, and infections that are not visible during a regular exam.
Why does my breath smell bad and how can I fix it?
Bad breath, or halitosis, can result from poor oral hygiene, certain foods, dry mouth, smoking, or medical conditions. Improve your oral hygiene, stay hydrated, and visit your dentist to address the underlying cause.
Why is dental work so expensive?
The cost reflects high-quality materials, advanced technology, skilled labor, and overhead costs of running a dental practice. Many dentists offer payment plans or financing options.